FDM & SLA
Fused Deposition Modeling & Stereolithography
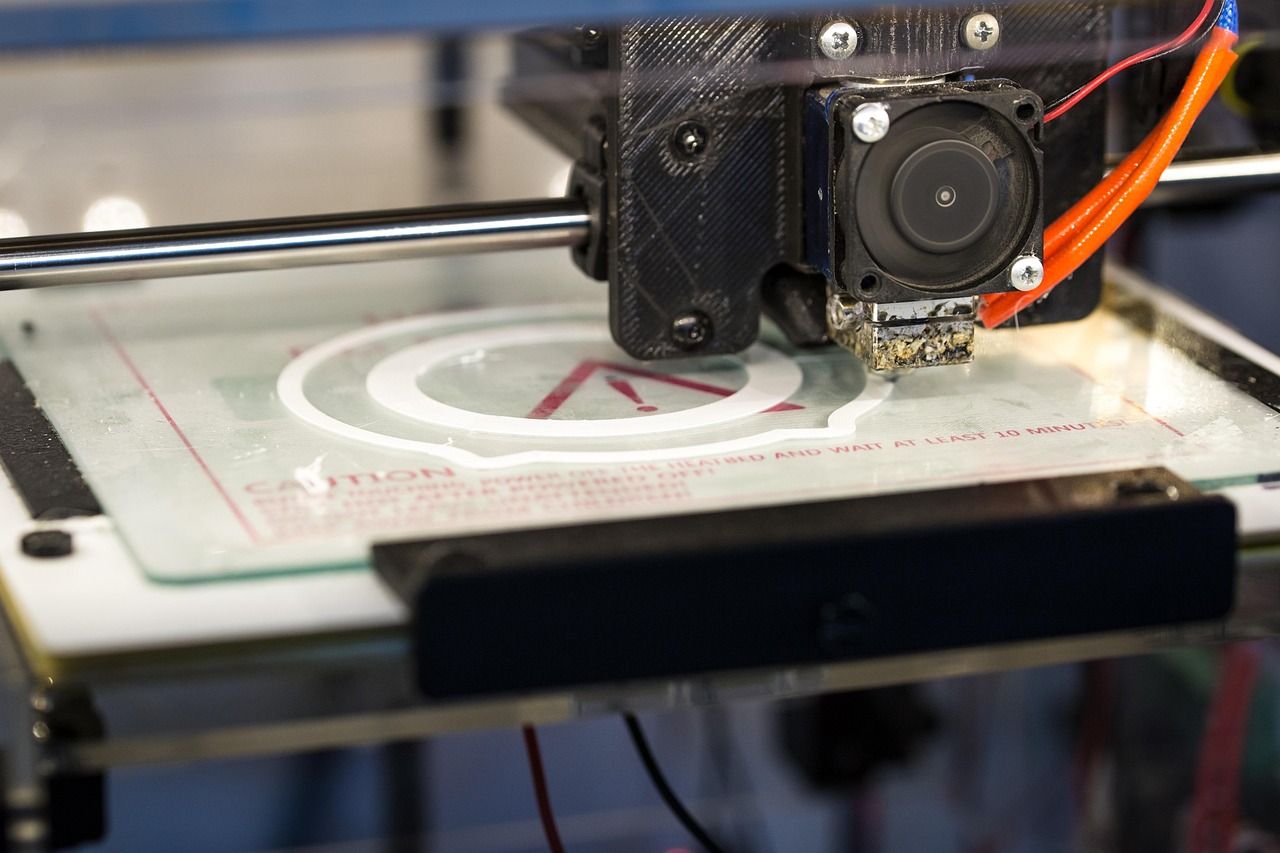
FDM
They work by melting plastic filament and laying it down one layer at a time to build a solid object. The process starts with a 3D CAD model, which is sliced into thin layers by software. The printer then heats the filament—usually PLA, ABS, or PETG—and pushes it through a nozzle that moves in precise patterns. As each layer cools, the next one is added on top until the full shape is formed. FDM printers are popular because they’re affordable, easy to use, and great for prototyping or making custom parts. FDM printers do not achieve the same amount of detail that resin printers do, but they’re reliable and versatile. From toys and tools to replacement parts and art projects, FDM printers make it easy to bring ideas to life!
SLA
Instead of melting plastic like FDM printers, SLA printers shine a laser into a vat of resin, hardening it layer by layer. This method allows for smooth surfaces, sharp edges, and fine details. This makes SLA printers ideal for printing jewelry, dental models, and prototypes that need a polished look. After printing, the object is rinsed and cured under UV light to strengthen it. SLA printers are popular in industries that require precision, such as engineering, and product design. Although they can be more expensive and require extra cleanup, their ability to produce professional-grade parts makes them worth it for many users. Whether you're printing a tiny gear or a lifelike figurine, SLA technology delivers impressive results.